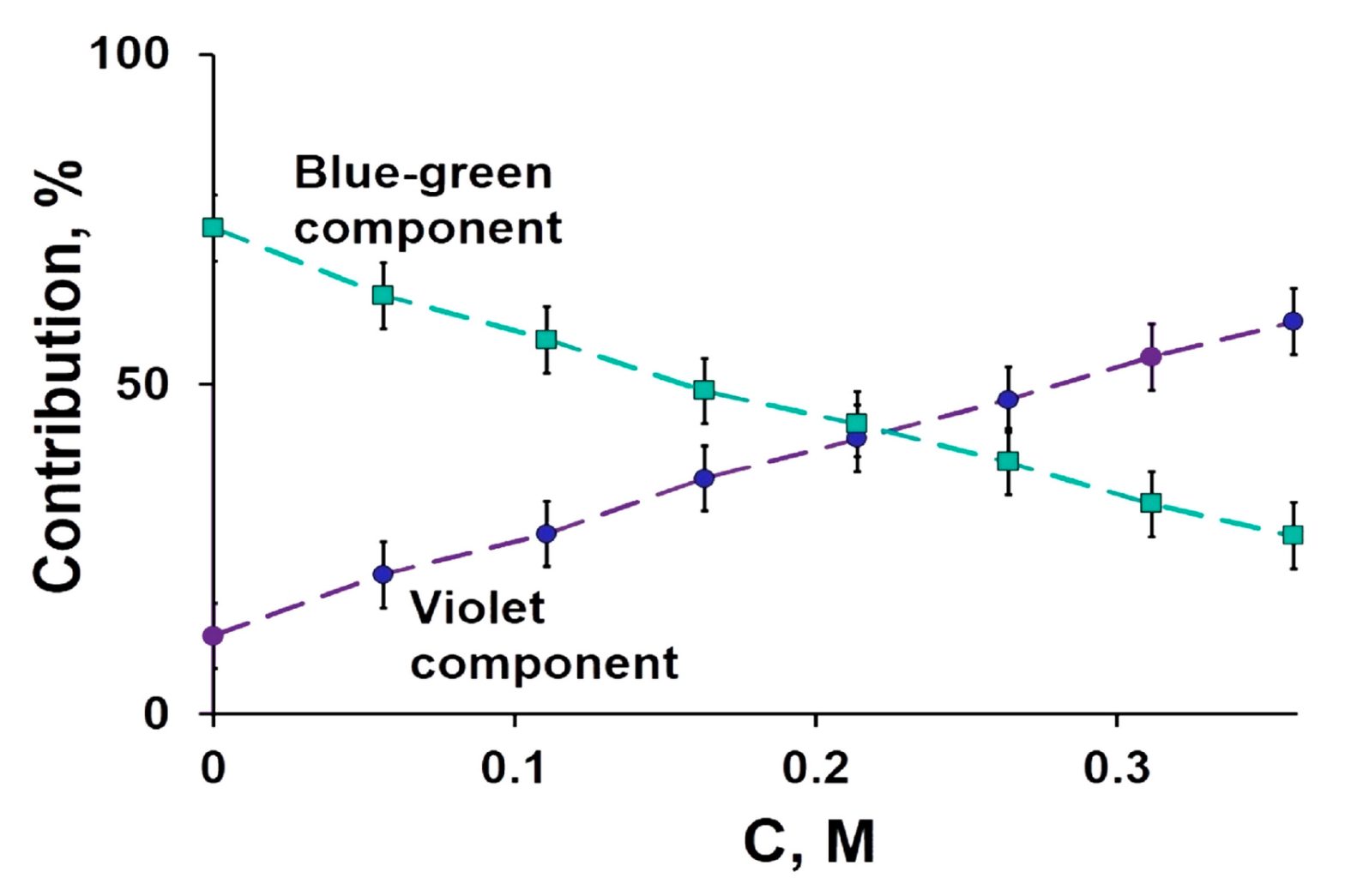
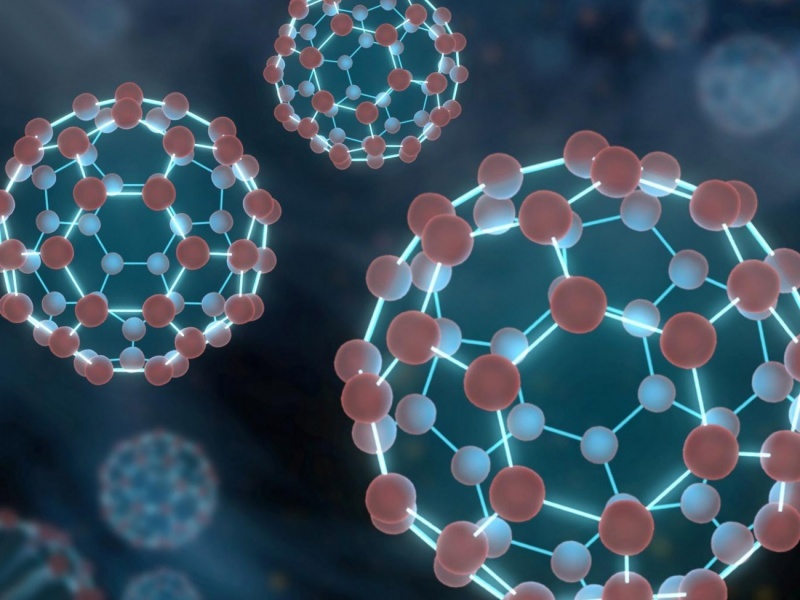
Fullerenes, as hydrophobic molecules, are limited in biomedical function due to their very low solubility. But taking C₆₀(OH)ₓ as an example, the properties of fullerenols were analyzed. It was found that fullerenols had good stability, water solubility, good biocompatibility and low cytotoxicity by adding a hydroxyl group to carbon atoms. In the biomedical field, it… Continue reading Biological and biocompatible characteristics of fullerenols nanomaterials for tissue engineering
Biological and biocompatible characteristics of fullerenols nanomaterials for tissue engineering