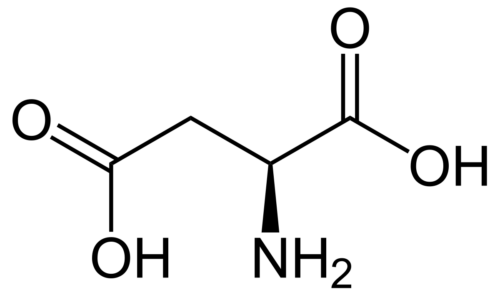
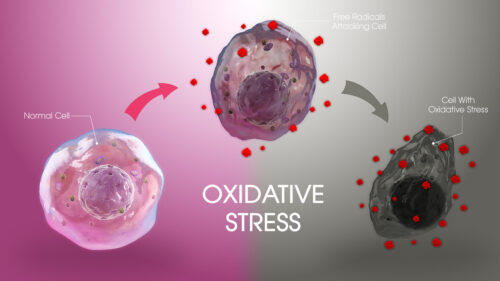
Multi-hydroxylated endohedral metallofullerenol [Gd@C(82)(OH)(22)](n) nanoparticles possess the general physico-chemical characteristics of most nanoparticles. They also exhibit uniquely low toxicity and antineoplastic efficacy. In the current study, the molecular mechanisms and epigenetic characteristics of the antineoplastic action of these nanoparticles are explored. Human breast cancer MCF-7 and human umbilical vein endothelial ECV304 cell lines were used. Cell viability assay, cell hierarchical cluster analysis by cDNA microarray, semi-quantitative reverse transcription-polymerase chain reaction and Western blot analysis were conducted to investigate the changes in molecular and cellular signaling pathways caused by [Gd@C(82)(OH)(22)](n). The results demonstrated the high antitumor activity and low cytotoxicity of [Gd@C(82)(OH)(22)](n) nanoparticles both in vivo and in vitro. Their possible anti-tumor mechanisms were also discussed. The present study may provide new insight into the mechanism of action of these nanoparticles.
Related researches 41 articles






![Biocompatible [60]/[70] Fullerenols: Potent Defense against Oxidative Injury Induced by Reduplicative Chemotherapy](https://biofullerene.com/wp-content/uploads/2022/11/istockphoto-65584859-356x356.jpg)