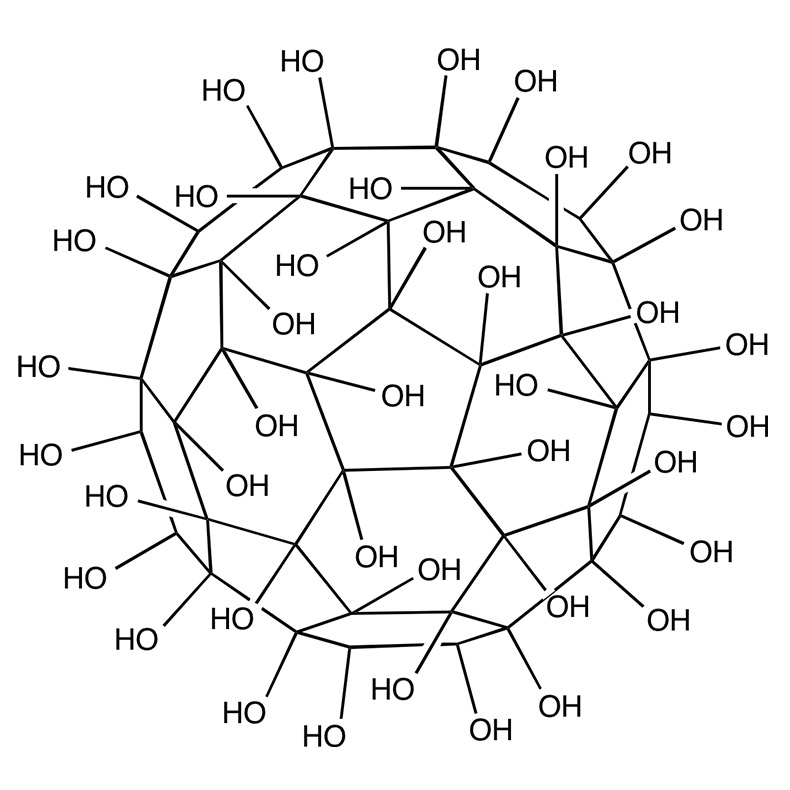
Fullerenols (polyhydroxylated fullerene C60) are nanomaterial with potentially broad applicability in biomedical sciences with high antioxidant ability, thus, we investigated the radioprotecting potential of fullerenol C60(OH)36#nbsp;on human erythrocytes irradiated by high-energy electrons of 6 MeV. The results demonstrate that C60(OH)36#nbsp;at concentration of 150 μg/mL protects the erythrocytes against the radiation-induced hemolysis (comparing to non-protected cells,… Continue reading Fullerenol C 60(OH) 36 protects human erythrocyte membrane against high-energy electrons
Fullerenol C 60(OH) 36 protects human erythrocyte membrane against high-energy electrons