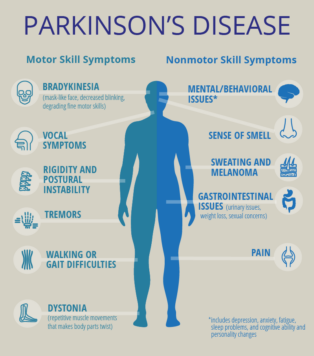
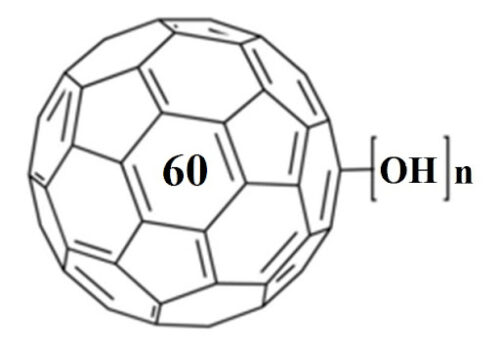
In an attempt to understand the possibility of applications of the fullerene-based systems for transporting various polar compounds like hexamethonium through the blood-brain barrier, we studied the influence of a series of derivatives of fullerene C60#nbsp;in the form of salts with hexamethonium bis-anion, namely the adducts of fullerenols with 6-aminohexanoic acid (IEM-2197), and two bis-adduct malonic acid derivatives of fullerene with addents bound in two hemispheres (IEM-2143) and in equatorial positions (IEM-2144), on model membranes. We showed that IEM-2197 induced the disintegration of the bilayers composed of DOPC at the concentrations more than 2 mg/ml. IEM-2144 and IEM-2143-induced ion-permeable pores at concentrations of 0.3 and 0.02 mg/ml, respectively; herewith, IEM-2143 was characterized by the greater efficiency than IEM-2144. IEM-2197 did not significantly affect the phase behavior of DPPC, while the melting temperature significantly decreased with addition of IEM-2144 and IEM-2143. The increase in the half-width of the main transition peaks by more than 2.0 °C in the presence of IEM-2144 and IEM-2143 was observed, along with the pronounced peak deconvolution. We proposed that the immersion of IEM-2144 and IEM-2143 into the polar region of the DOPC or DPPC bilayers led to an increase in the relative mobility of tails and formation of ion-permeable defects. IEM-2197 demonstrated the more pronounced effects on the melting and ion permeability of PG- and PS-containing bilayers compared to PC-enriched membranes. These results indicated that IEM-2197 preferentially interacts with the negatively charged lipids compared to neutral species.
Related researches 71 articles












![Inhalable gadofullerenol/[70] fullerenol as high-efficiency ROS scavengers for pulmonary fibrosis therapy](https://biofullerene.com/wp-content/uploads/2022/12/istockphoto-12925559-440x356.jpg)














![Palladium-Catalyzed Reaction of [60]Fullerene with Aroyl Compounds via Enolate-Mediated sp 2 C-H Bond Activation and Hydroxylation](https://biofullerene.com/wp-content/uploads/2022/12/2978543-356x356.png)