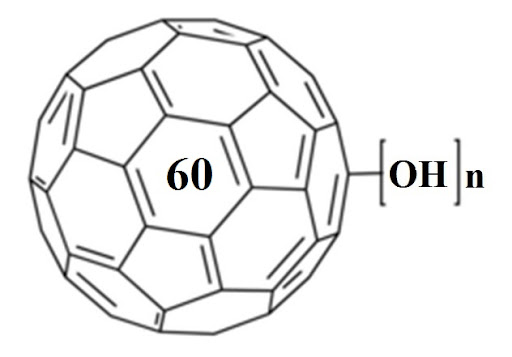
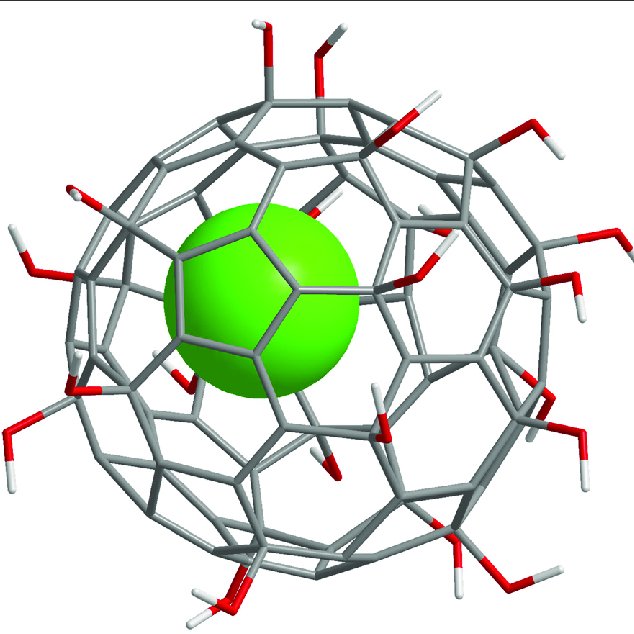
While exploring articles on the National Library of Medicine’s website, we stumbled upon a gem of a paper that’s almost like a grand tour through the evolution of fullerenols! The article, titled “Potential Medical Use of Fullerenols After Two Decades of Oncology Research,” can be found here – https://journals.sagepub.com/doi/10.1177/15330338231201515. It’s a goldmine of information! Before… Continue reading Exploring the World of Fullerenols: A Deep Dive into Their Potential Medical Use
Exploring the World of Fullerenols: A Deep Dive into Their Potential Medical Use