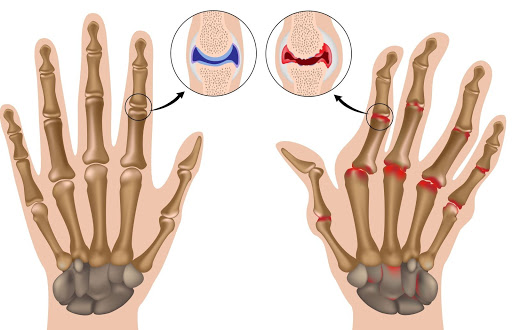
Accumulated evidence suggests a pathogenic role of reactive oxygen species (ROS) in perpetually rheumatoid joints. Therefore, the application of radical scavengers for reducing the accumulation of ROS is beneficial for patients with rheumatoid arthritis (RA). We synthesized water-soluble fullerenols that could inhibit the production of ROS and applied intra-articular (i.a.) injection in an experimental arthritis… Continue reading Amelioration of Experimentally Induced Arthritis by Reducing Reactive Oxygen Species Production through the Intra-Articular Injection of Water-Soluble Fullerenol
Amelioration of Experimentally Induced Arthritis by Reducing Reactive Oxygen Species Production through the Intra-Articular Injection of Water-Soluble Fullerenol