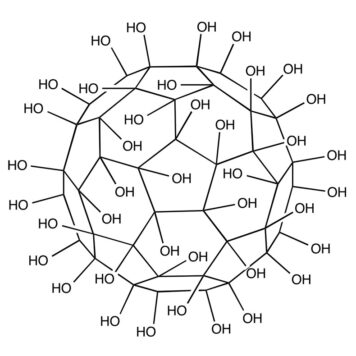
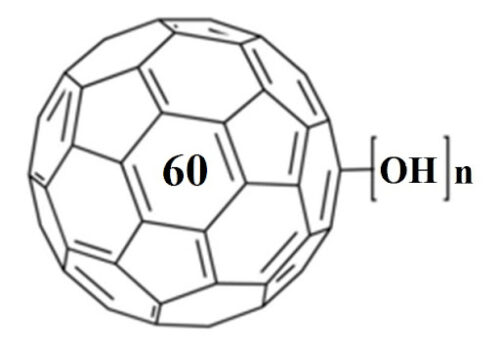
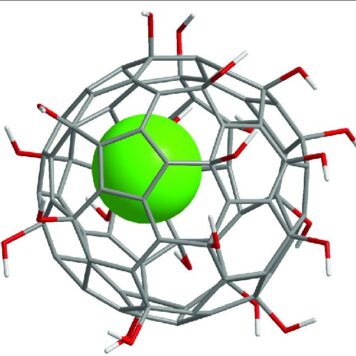
Age-related macular degeneration (AMD) causes central vision impairment with increased incidence. In the pathogenesis of AMD, reactive oxygen species (ROS) are associated with RPE cell apoptosis. H2O2 is an oxidative toxicant and is used to establish the AMD in vitro model. However, the mechanisms of ROS in H2O2-induced AMD are still unclear. Fullerenol, a promising antioxidant of nanomaterials, protects RPE cells from ROS attack. In addition to working as a scavenger, little is known about the antioxidant mechanism of fullerenol in RPE cells. In this study, transcriptome sequencing was performed to examine the global changes in mRNA transcripts induced by H2O2 in human ARPE-19 cells. Moreover, we comprehensively investigated the protective effects of fullerenol against H2O2-induced oxidative injury by RNA sequencing. Gene Ontology enrichment analysis showed that those pathways related to the release of positive regulation of DNA-templated transcription and negative regulation of apoptotic process were affected. Finally, we found that 12 hub genes were related to the oxidative-protection function of fullerenol. In summary, H2O2 affected these hub genes and signaling pathways to regulate the senescence of RPE cells. Moreover, fullerenol is a potent nanomaterial that protects the RPE and would be a promising approach for AMD prevention.
Related researches 71 articles












![Inhalable gadofullerenol/[70] fullerenol as high-efficiency ROS scavengers for pulmonary fibrosis therapy](https://biofullerene.com/wp-content/uploads/2022/12/istockphoto-12925559-440x356.jpg)














![Palladium-Catalyzed Reaction of [60]Fullerene with Aroyl Compounds via Enolate-Mediated sp 2 C-H Bond Activation and Hydroxylation](https://biofullerene.com/wp-content/uploads/2022/12/2978543-356x356.png)