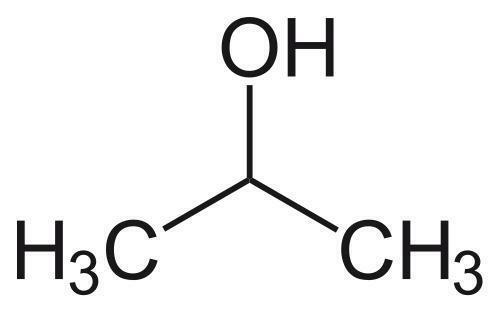
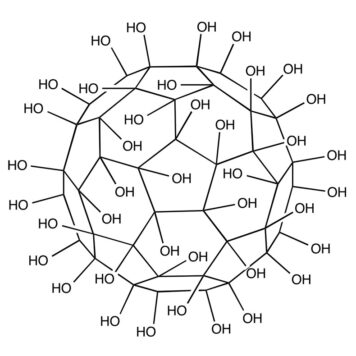
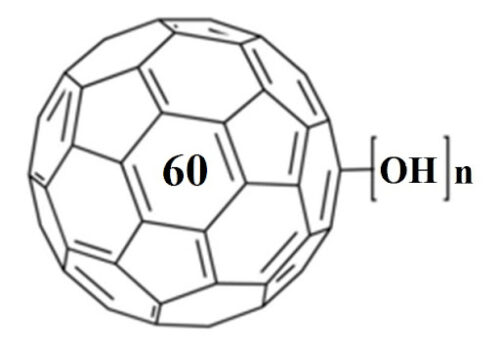
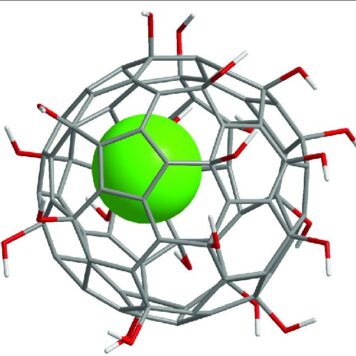
Pulmonary fibrosis has become a fatal disease for its high incidence and few effective drugs available in clinic. In this study, gadofullerenol (GF-OH) and [70] fullerenol (C70-OH) nanoparticles (NPs) prepared by a one-pot reaction were designed as nanomedicines to treat this fatal disease. It was revealed that the inhalation of gadofullerenols and [70] fullerenols substantially alleviates the collagen deposition induced by acute lung injury. Based on detailed studies of oxidative stress parameters and transforming growth factor-β1#nbsp;(TGF-β1), we demonstrated they owned the antioxidant and anti-inflammatory functions for the modulation of ROS-mediated inflammation process. Thus the therapeutic effect may be associated with synergistic mechanism of scavenging free radicals and indirectly modulating TGF-β1#nbsp;expression. Moreover, GF-OH NPs were observed to show the superiority to C70-OH NPs both in vitro and in vivo due to the structural distinction. These results suggest the inhalable fullerenols are highly potential for clinical therapy of pulmonary fibrosis.
Related researches 71 articles


























![Palladium-Catalyzed Reaction of [60]Fullerene with Aroyl Compounds via Enolate-Mediated sp 2 C-H Bond Activation and Hydroxylation](https://biofullerene.com/wp-content/uploads/2022/12/2978543-356x356.png)