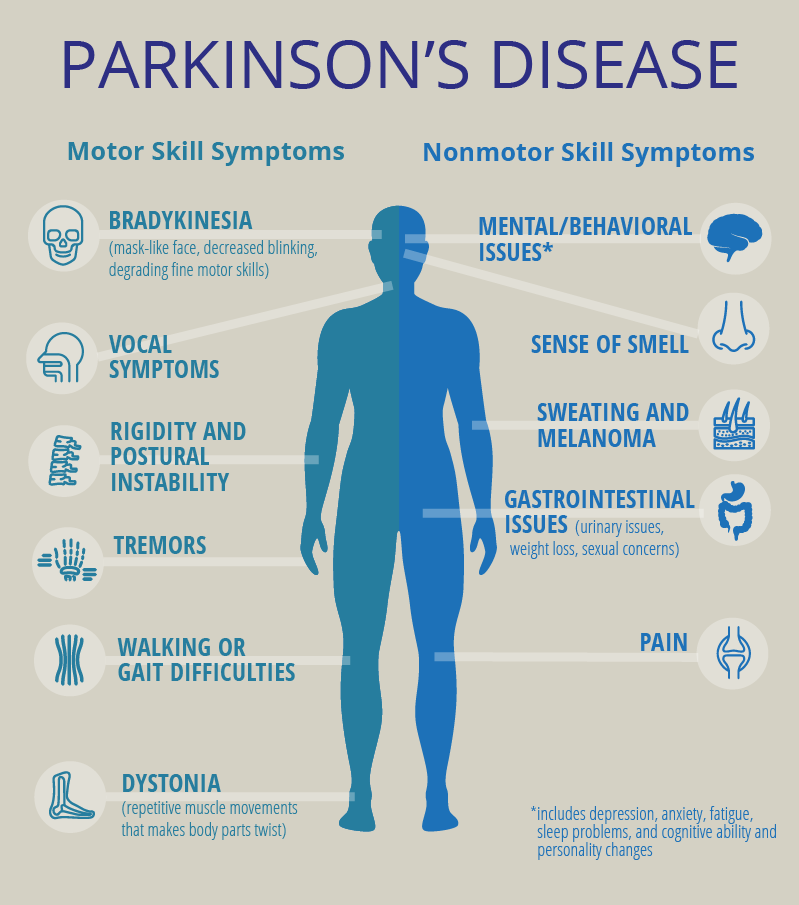
Abstract Neuroprotective properties of fullerenols С60(OH)30#nbsp;and С70(OH)30#nbsp;have been shown in a Drosophila melanogaster model of Parkinson’s Disease (PD). Fullerenols used in this work demonstrated negligible toxicity even at high concentrations as a result of a specifically developed manufacturing process. It has been shown that the drugs promote restoration of dopamine levels, reduce oxidative stress in… Continue reading The neuroprotective effect of fullerenols on a model of Parkinson’s disease in Drosophila melanogaster
The neuroprotective effect of fullerenols on a model of Parkinson’s disease in Drosophila melanogaster